Introduction
The world of investing can seem complex, with endless options and strategies. For new investors, the idea of picking individual stocks can be intimidating, as a single bad decision can have a significant impact on your portfolio. Fortunately, there is a powerful, low-cost solution that offers instant diversification and simplicity: Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs). These funds have revolutionized how millions of people approach the stock market, making it easier than ever to build a resilient and diverse portfolio. An ETF is a cornerstone of modern financial planning, providing a straightforward way to invest in a broad range of assets without the complexity of traditional mutual funds. This comprehensive guide will demystify ETFs, explaining how they work, their key benefits, the different types available, and how you can use them to build a powerful long-term investment strategy.
What Exactly is an Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF)?
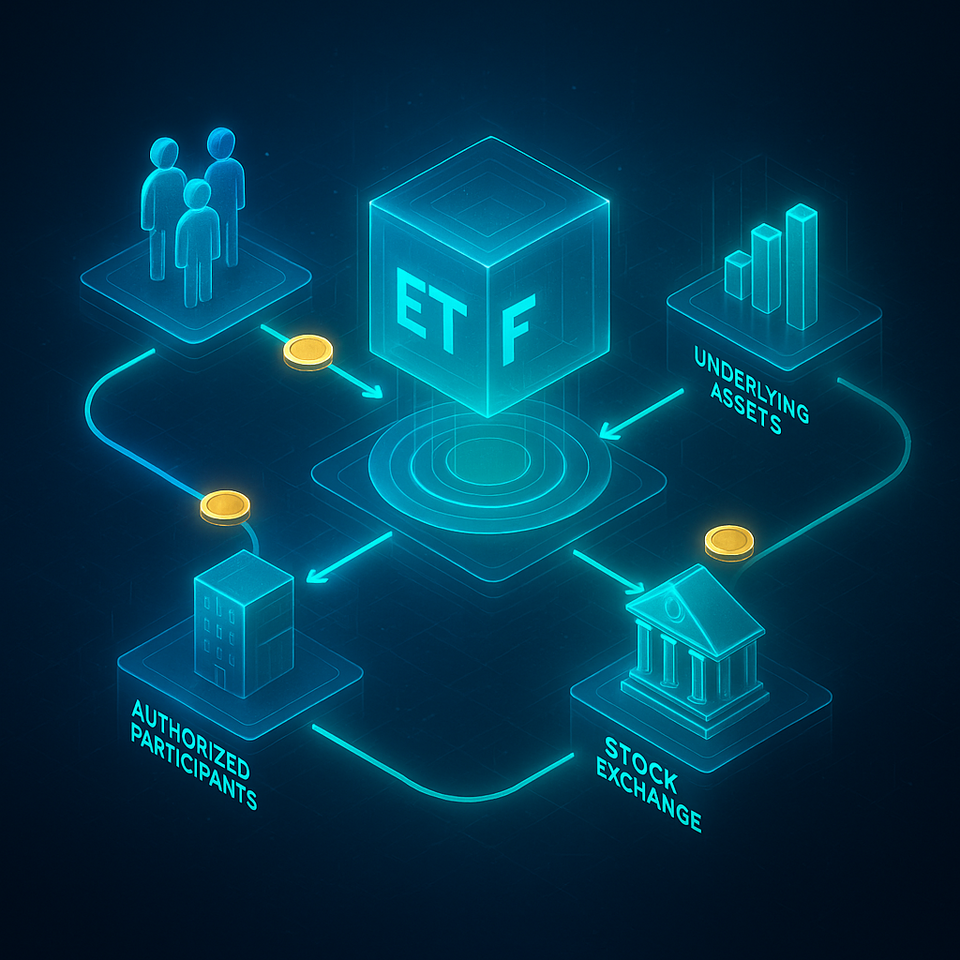
An ETF is a type of investment fund that holds a collection of stocks, bonds, or other assets. It’s similar to a mutual fund in that it pools money from multiple investors to buy a variety of securities. However, a key difference is that an ETF trades on a stock exchange, just like a regular stock. This means you can buy and sell ETF shares throughout the trading day at a market-determined price, which is constantly fluctuating.
Passive vs. Active Management
Most ETFs are passively managed. This means the fund’s manager isn’t actively trying to beat the market; instead, they simply aim to track the performance of a specific market index. For example, an S&P 500 ETF holds all the stocks in the S&P 500 in the same proportions. This passive approach is what allows ETFs to have incredibly low fees. While there are some actively managed ETFs, the vast majority are passive.
The Key Benefits of Investing in ETFs
ETFs have become so popular because they offer several significant advantages over traditional investing methods.
1. Instant Diversification
This is the most powerful benefit for beginners. With a single purchase of an ETF, you can own a piece of dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of different companies. This instant diversification significantly reduces your risk. If one company in the fund performs poorly, it won’t have a major impact on your entire portfolio. This contrasts sharply with buying a single stock, where a company’s poor performance can be devastating.
2. Low Costs
Because most ETFs are passively managed, they have very low expense ratios. An expense ratio is the annual fee you pay as a percentage of your total investment. While a typical actively managed mutual fund might have an expense ratio of 1% or more, a passively managed ETF might be as low as 0.03%. Over a long investing horizon, this difference in fees can add up to tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars in your pocket.
3. Tax Efficiency
ETFs are generally more tax-efficient than mutual funds. Because they have very low turnover (they don’t buy and sell assets frequently), they tend to generate fewer capital gains for investors. This means you are less likely to get hit with a surprise tax bill. This is a significant advantage for those who invest in a taxable brokerage account.
4. Liquidity and Flexibility
Since ETFs trade on an exchange, you can buy or sell them at any time during market hours. This flexibility allows you to react quickly to market changes or to simply make a transaction when it is most convenient for you. This is a stark contrast to mutual funds, which only trade once per day after the market closes.
Types of ETFs: A World of Options
The ETF market has grown to include a wide variety of funds that track different sectors and assets.
1. Broad Market ETFs
These are the most popular and best for beginners. They track a major market index like the S&P 500 (U.S. large-cap companies), the Nasdaq 100 (U.S. technology companies), or a total world stock market index. They provide a simple way to get broad market exposure.
2. Sector ETFs
These funds focus on a specific industry or sector, such as technology, healthcare, or consumer goods. They can be a good way to invest in a sector you believe will outperform but come with a higher level of risk than a broad market ETF.
3. Bond ETFs
These funds hold a basket of bonds. They can provide a steady income stream and are typically less volatile than stock ETFs, making them a great tool for balancing a portfolio as you get older.
4. International ETFs
These funds allow you to easily invest in markets outside of your home country. They can be a great way to diversify your portfolio and take advantage of global growth opportunities.
5. Specialty ETFs
The market is full of specialized ETFs that focus on everything from commodities like gold to specific investment themes. These are typically for more advanced investors.
Building Your Portfolio with ETFs
For a beginner, building a powerful portfolio with ETFs is a straightforward process. The goal is to build a core, well-diversified portfolio that is low-cost and designed for the long term.
Step 1: Start with a Broad Market ETF
Begin by investing in a low-cost, broad market ETF. An S&P 500 ETF or a total stock market ETF is an excellent choice for a core holding.
Step 2: Add International and Bond ETFs
To further diversify, you can add an international stock ETF and a bond ETF to your portfolio. This balance of domestic and international stocks, along with the stability of bonds, will create a much more resilient portfolio.
Step 3: Rebalance Periodically
Over time, your portfolio’s allocation will drift. If stocks perform well, they might make up a larger percentage of your portfolio than you originally intended. Periodically, you should rebalance your portfolio—sell a small portion of your high-performing assets and buy more of your underperforming assets to bring your portfolio back to your target allocation.
Conclusion
Exchange-Traded Funds have democratized investing, making it easier and more affordable than ever for anyone to build a well-diversified portfolio. Their low costs, instant diversification, and flexibility make them an ideal tool for beginners and experienced investors alike. By understanding how they work and building a core portfolio with broad market ETFs, you can take a significant step toward achieving your financial planning goals. Remember, successful investing is not about timing the market; it’s about time in the market. ETFs provide a simple and powerful way to stay the course and build lasting wealth.



